Laser surgery is a surgical procedure that uses a laser beam to cut, ablate (remove), vaporize, or coagulate tissue. This surgery uses focused light beams to perform surgical procedures, offering precision and reduced tissue damage compared to traditional methods, with applications ranging from correcting vision to treating skin conditions and removing tumors.
How It works?
Lasers emit a concentrated beam of light that can be focused to a very small area, allowing for precise and controlled tissue manipulation.
What are its benefits?
- Smaller incisions: This results in less pain, faster recovery, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery.
- Shorter hospital stays: Patients often recover faster and can go home sooner.
- Reduced risk of complications: Minimally invasive surgery can lead to a lower risk of infections and other complications.
Few examples of laparoscopic surgeries:
I. Hernia Repair:
Hernia repair surgery, or herniorrhaphy, involves surgically correcting a hernia, where an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak area in the abdominal wall, and can be performed using open or laparoscopic (keyhole) techniques, often with mesh reinforcement to strengthen the area. Based on the area of surgery it is classified into:
1. Inguinal Hernia:
An inguinal hernia, or groin hernia, is a condition where abdominal tissue or part of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, often in the groin area. It’s typically a bulge that can be painful and may worsen with activity or coughing.
2. Umbilical Hernia:
An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall near the belly button, often appearing as a soft bulge. While common in infants, they can also develop in adults and usually require surgical repair if they become problematic.
3. Incisional Hernia:
An incisional hernia happens when the abdominal muscles, which were previously cut and stitched during surgery, weaken over time, allowing internal organs or tissues to bulge through the weakened area. It’s a common complication of abdominal surgery, where the surgical incision compromises the integrity of the abdominal wall.
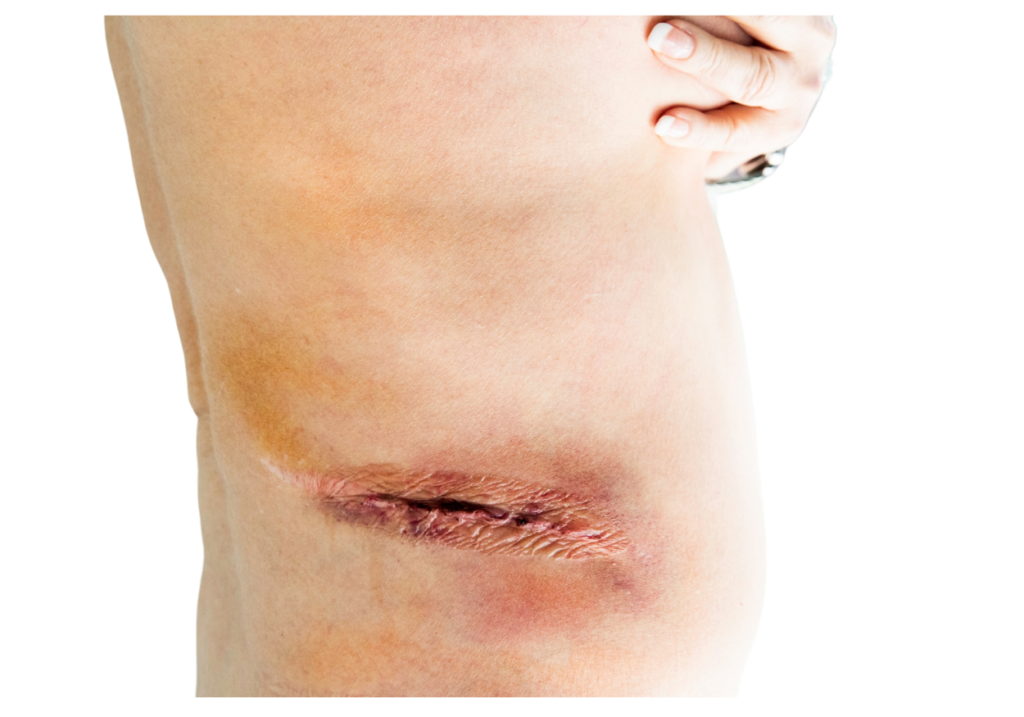
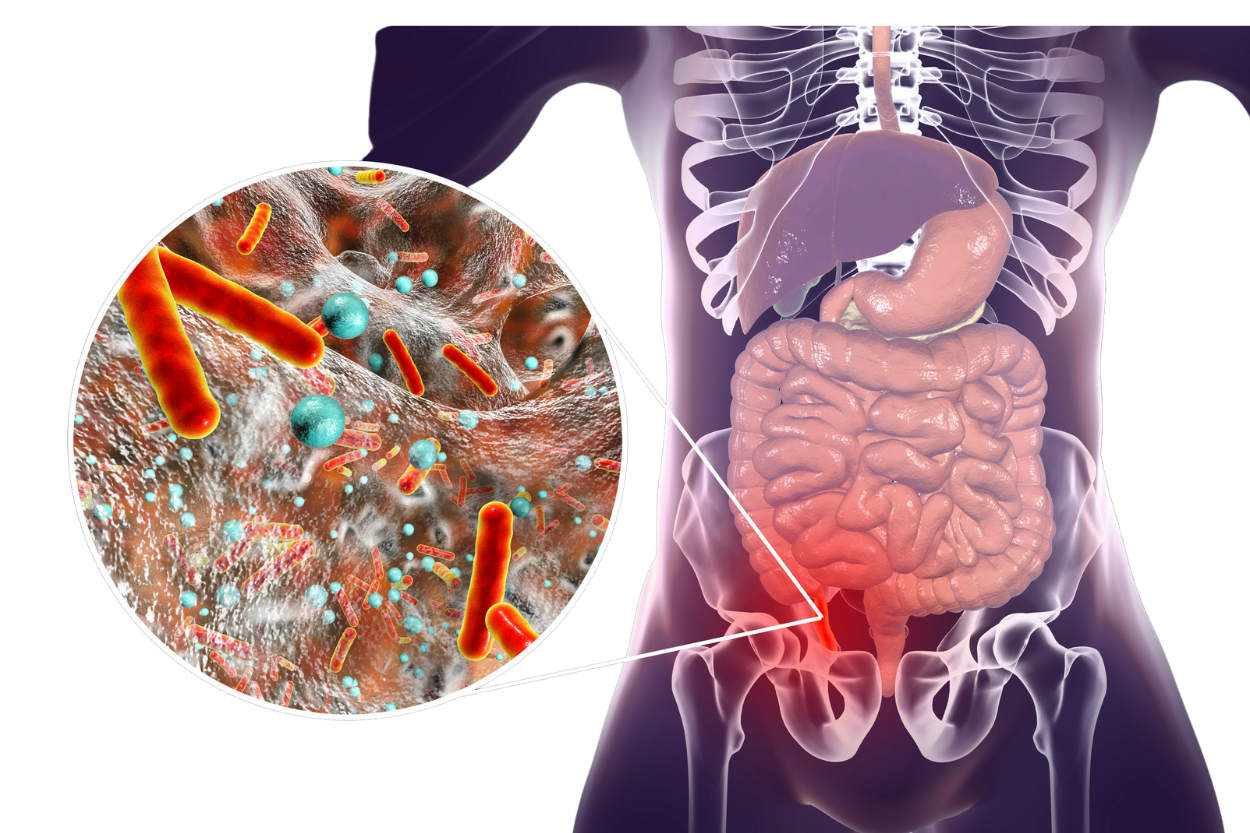
An appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix, which is located in the right lower side of the abdomen. This operation is usually carried out on an emergency basis to treat appendicitis (inflamed appendix). This may occur as a result of an obstruction in part of the appendix.
II. Appendectomy (appendix removal):
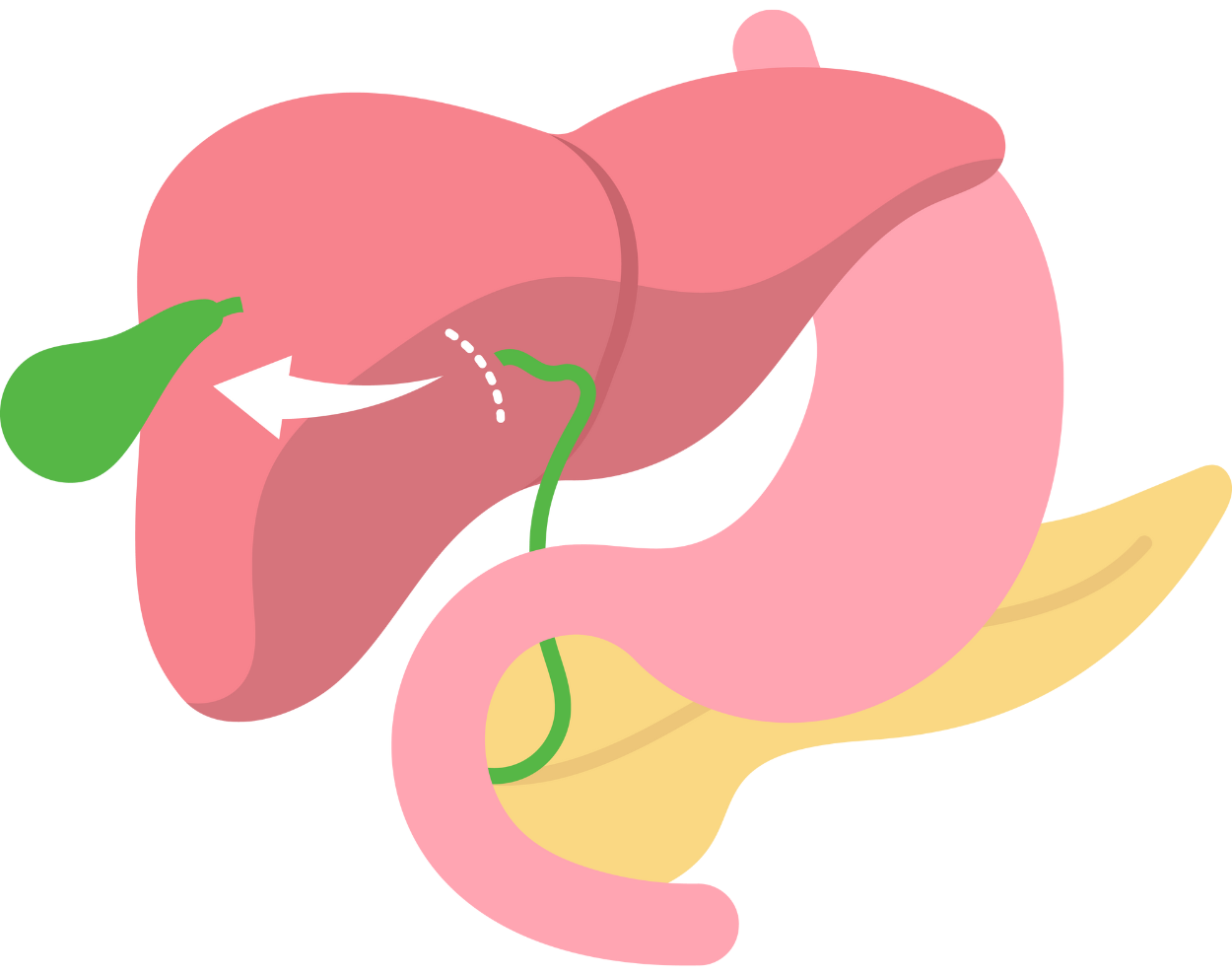
Cholecystectomy, or gallbladder removal surgery, is a common procedure to treat gallstones and related gallbladder problems. It can be performed using laparoscopic (keyhole) or open surgery techniques, with laparoscopic surgery being the most common approach.
III. Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal):
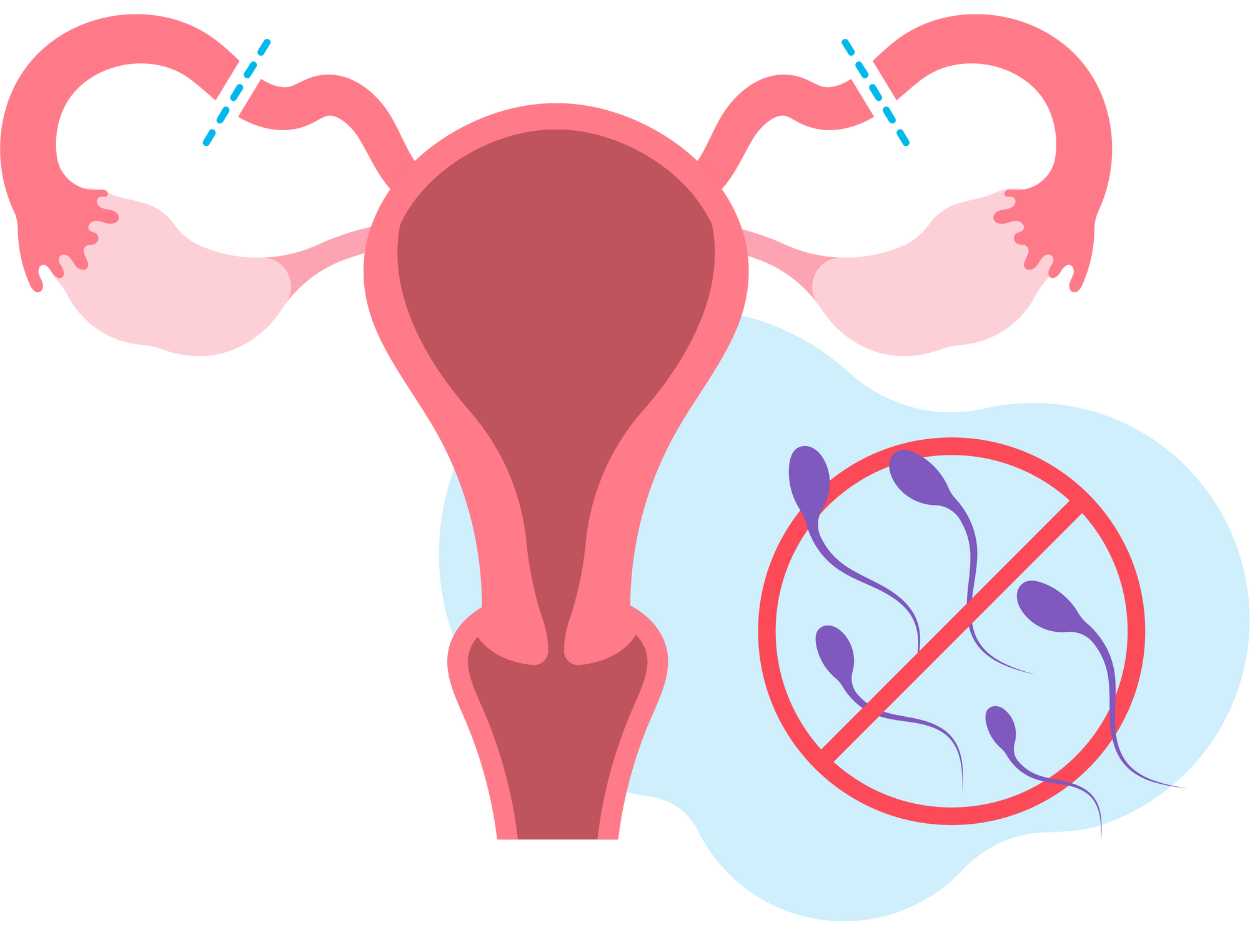
Tubectomy, also known as tubal ligation or “getting your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure that permanently prevents pregnancy by blocking or sealing a woman’s fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from being fertilized
IV. Tubectomy (Female sterilization) :
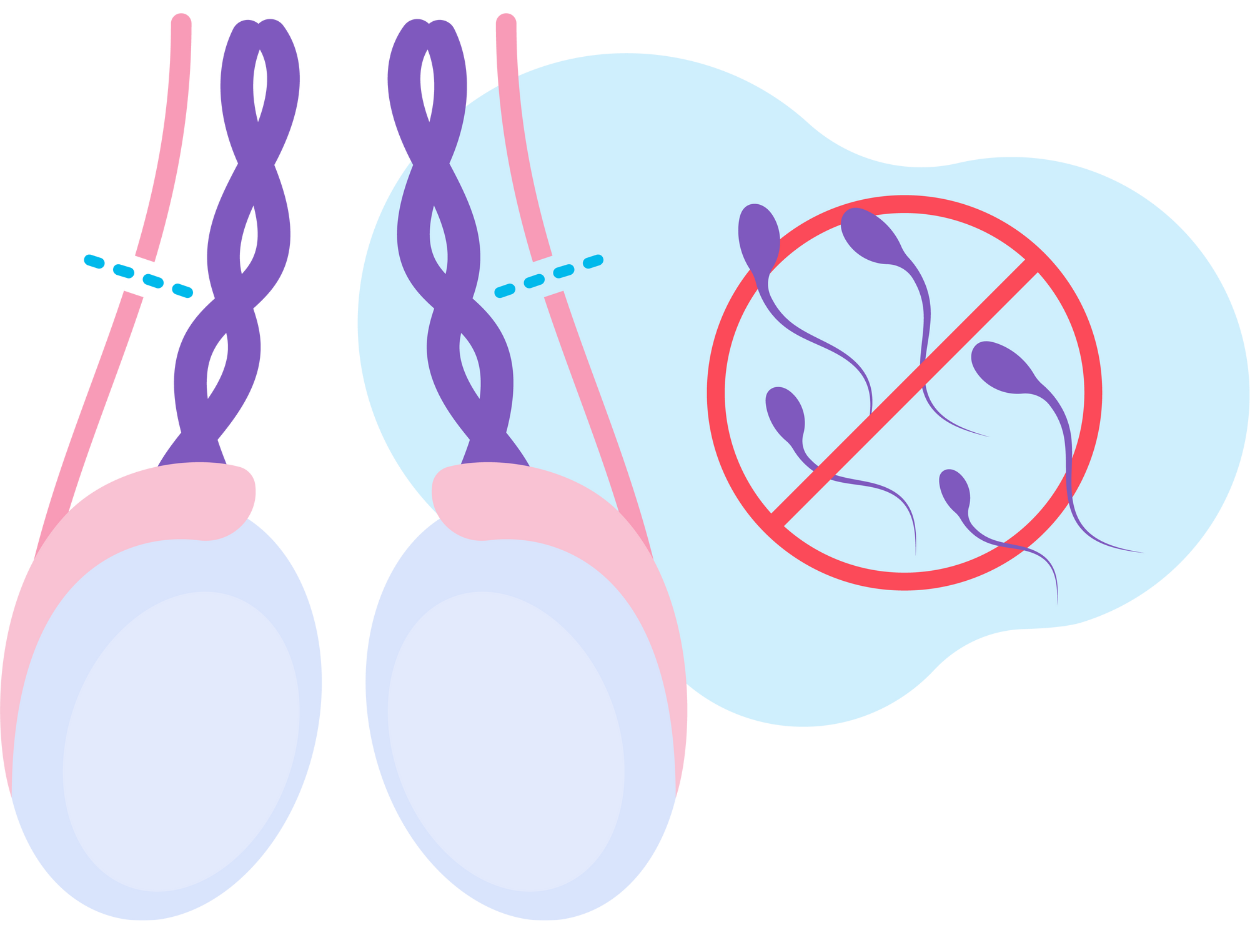
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure for male sterilization that involves cutting and sealing the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles, preventing sperm from being released during ejaculation